Large and long-lasting shaking at dawn (November 22). 。 。 It's been a big earthquake since a long time. Fortunately, there seems to be no direct human damage related to life and death so far, but it was a morning when I was reminded of Japan, a country with many disasters (earthquakes, tsunamis, typhoons, etc.).
For Japan, where the number of foreign tourists is rapidly increasing, it is of course important to introduce content such as history and culture, but also to provide information on disaster preparedness and safety in Japan, especially earthquakes and typhoons. It is also important to give a sufficient explanation of the safety in Japan to inbound tourists who are unfamiliar with disasters, and to have them visit with peace of mind in the future.
It seems that the earthquake has subsided, so when I cross Minami Takahashi near my house for work, the sluice gate from the Kamejima River, which should normally open, to the Sumida River, is closed on a street such as the Nihonbashi Cruise. Is it prepared for the tsunami? (The Japan Meteorological Agency sent tsunami advisory to Uchibo and Izu Islands in Chiba Prefecture at 7:26 am.)
The Kamejima River Sluice Gate is a tide gate created to protect the Kamejima River basin from storm surge damage. The downtown area of Tokyo, which has developed by reclaiming the Hibiya cove since the Edo period, has long been a lot of storm surges and tsunamis. I've been suffering from flood damage. Chuo-ku is also located in areas with relatively low ground heights, and is no exception in this case.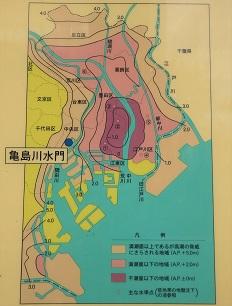
For example, there is a story called "Tsunami" in Seicho Matsumoto's short story book "Mujukujinbetsu Book" (Bunshun Bunko), which was introduced in a blog post I wrote earlier (/archive / 2014/06/post-2075.html), but here, a tsunami depicts a people's footing in Ishikawajima during the Edo period. After the Meiji era, coastal areas such as the Sumida River in the eastern lowland of Tokyo became flooded areas such as floods and storm surges, and storm surge countermeasures were promoted after severe damage such as the Kitty Typhoon (1949) that hit the Kanto area. Will be
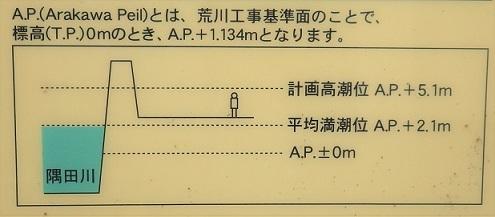
In particular, the storm surge of A.P. + 5.02m in the Nagoya area due to the typhoon in Ise Bay in 1960 (A.P. is "Arakawa Construction Standard Surface". It is determined at the lowest water level of water level station, Reigishi Island in Shinkawa. See the figure above. In the 1960s, the construction of seawalls, the so-called razor dike, began in Tokyo. The Kamejima River Sluice Gate was also completed in 1969 at this time. The gate of the sluice gate is 8.3m, which can prevent storm surges from entering the Kamejima River as well as seawalls. As a result of these measures, when Typhoon No. 20 hit in October 1979, a storm surge (A.P + 3.55m) exceeding the Kitty Typhoon was recorded, but the lives of the local residents were protected without breaching.
It was a Kamejima River sluice gate that I rarely see, but as in this case, when a tsunami or storm surge occurred due to an earthquake or typhoon, etc. and the water level of the river rises, the sluice was closed as soon as possible to prevent flooding and protect the safety of residents and visitors to Chuo-ku. .
[Kamejima River Sluice Gate]
Location 2-31-22 Shinkawa, Chuo-ku, 104-0033, Japan
![]() fun time
fun time![]()
![]()


![]()
![]()
![]()








